Pediatric Fractures ( Fractures In Children)

Treatment options may include:
Blogs
FAQs
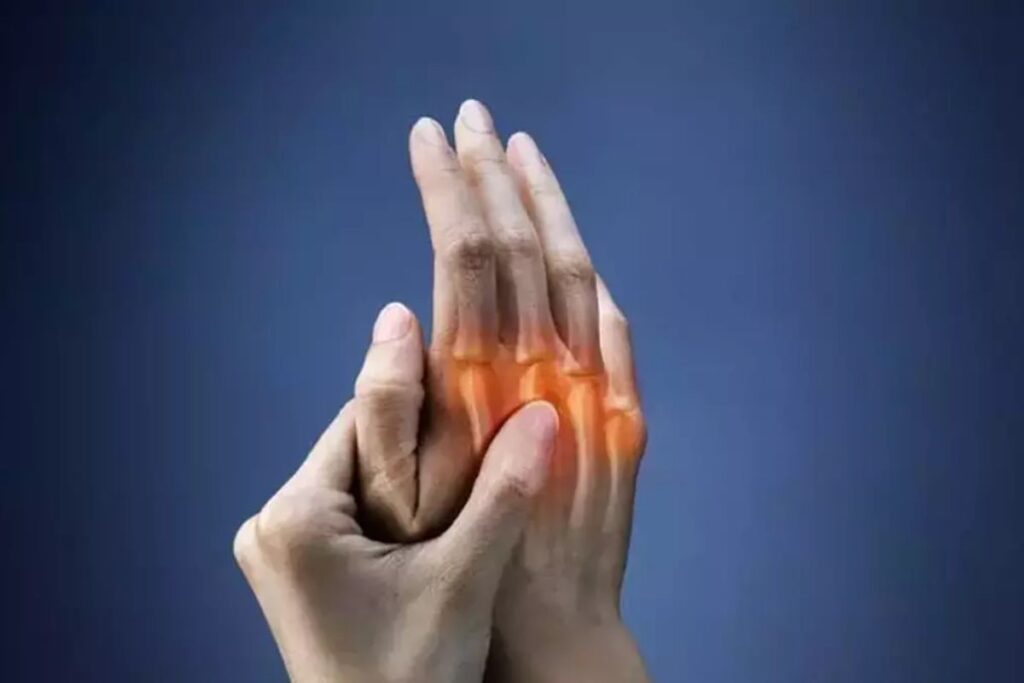
What is Arthritis?
The definition of arthritis is “joint inflammation.” More than 100 rheumatic diseases and other ailments that cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling are together referred to as arthritis.
In addition to gradually deteriorating our bones, tissues, and joints, rheumatoid arthritis also harms the lining around our joints.
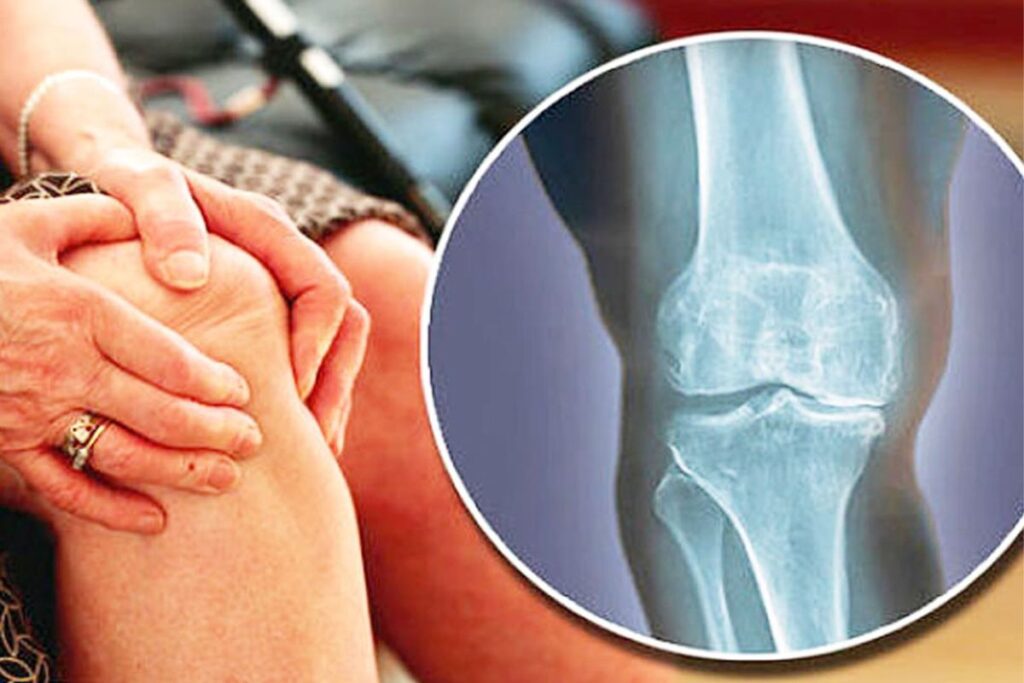
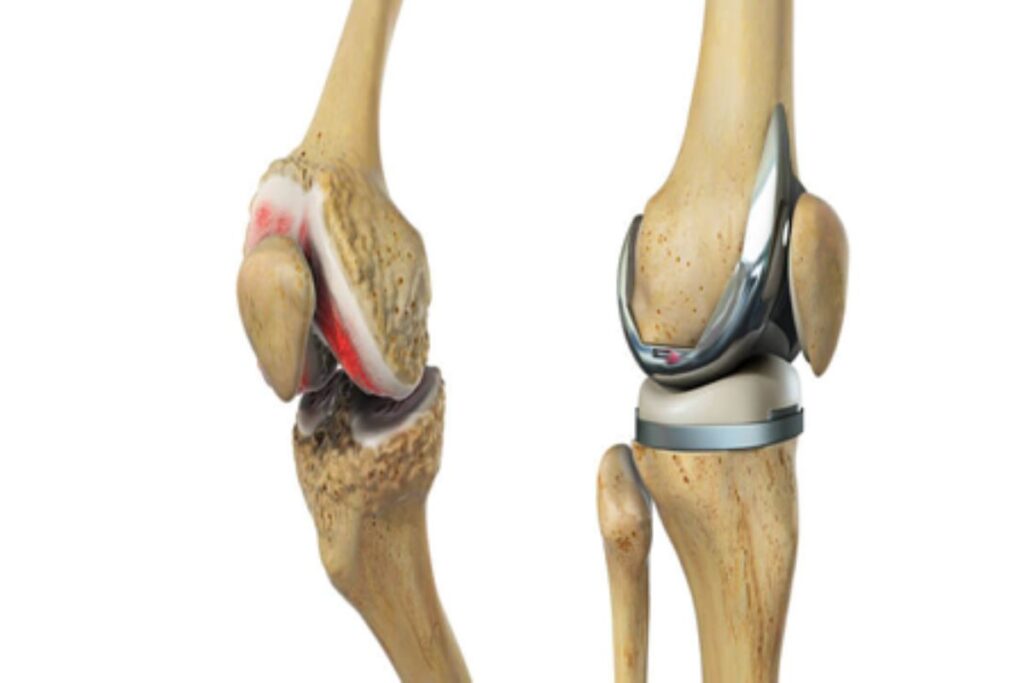
Osteoarthritis, a disorder that worsens with time and is frequently found in the hip, knee, and spine, slowly destroys the cartilage that surrounds the ends of bones.
What causes Arthritis?
Arthritis is a degenerative condition where the articular cartilage that protects the ends of bones begins to break down over time, much as how the treads of your tires wear down over time. Arthritis can have a variety of reasons. An estimated 30–40 million Americans suffer from arthritis, and the majority of these tears are brought on by degenerative arthritis (osteoarthritis). Rheumatoid arthritis with inflammation affects 2–3 million Americans. One of the main causes of arthritis in younger people is trauma to the knee. Most frequently, arthritis worsens with age.
How do I keep up my Orthopedic Health?
Simple dietary and lifestyle adjustments can help you prevent significant orthopedic issues. Avoid engaging in repetitive motions that strain your joints, such as deep knee bends. Regularly visit the doctor. A wonderful strategy to monitor your orthopedic health is to see your primary care physician annually. This is crucial for older adults since they are more prone to get injured and develop arthritis.
After having a minimally invasive partial knee replacement, may I resume my typical activities?
Once they have recovered sufficient strength and flexibility and their orthopaedic surgeon has given them the all-clear to start routine activities, the majority of patients can resume normal activities after partial knee replacement. Running, jumping, and twisting are all repetitive joint jarring activities that should be avoided. Many patients have resumed their previous hobbies after partial knee replacement surgery, including gardening, swimming, golf, and doubles tennis.