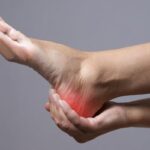
Arthritis is a common medical condition that affects millions of people around the world. While it is often associated with the hands, knees, and hips, arthritis can also target the smaller joints in the body, including those in the foot and ankle. Arthritis of the foot and ankle can be a source of significant discomfort and mobility issues. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various forms of arthritis that can impact these joints, the symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Understanding Arthritis of Foot and Ankle
Arthritis is a term that refers to inflammation of the joints. It encompasses over 100 different types, with the most common forms being osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the most prevalent form of arthritis and often referred to as “wear-and-tear” arthritis. It results from the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility. OA can affect any joint, including those in the foot and ankle.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): RA is an autoimmune disease where the body’s immune system attacks its own joints. It can affect joints throughout the body, including those in the foot and ankle. RA often leads to inflammation, pain, and joint deformities.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: This form of arthritis develops after an injury to the foot or ankle. It can occur years or decades following the initial injury, resulting in pain, swelling, and reduced joint function.
Symptoms of Arthritis in the Foot and Ankle
Arthritis of the foot and ankle can present with a variety of symptoms, which may include:
- Pain: Persistent pain in the affected joint, often worsening with activity or at the end of the day.
- Stiffness: Reduced joint flexibility and increased stiffness, making it challenging to move the affected foot or ankle.
- Swelling: Inflammation and swelling of the joint can occur, leading to discomfort and a feeling of tightness.
- Deformities: Over time, arthritis can lead to joint deformities, such as bunions or hammer toes, which can affect foot function and appearance.
- Instability: A sense of joint instability and a tendency to “give way” can occur due to the loss of joint integrity.
- Difficulty Walking: As the condition progresses, difficulty walking, running, or engaging in physical activities can become more pronounced.
- Crepitus: A sensation of grating or grinding in the joint can be experienced during movement.
Diagnosis of Foot and Ankle Arthritis
Diagnosing arthritis in the foot and ankle involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Here are some of the steps involved:
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, when they started, and any previous injuries or conditions that may be contributing to your joint issues.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected foot and ankle will be conducted to assess range of motion, joint stability, and any visible deformities.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans may be ordered to visualize the joint and assess the extent of damage and inflammation.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for inflammation and to help diagnose autoimmune forms of arthritis like RA.
Treatment Options for Foot and Ankle Arthritis
The management of arthritis in the foot and ankle aims to relieve pain, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and pain relievers can help manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is an essential component of treatment, as it focuses on improving joint flexibility, strength, and overall function.
- Orthotics and Supportive Devices: Custom orthotics, braces, and footwear modifications can provide support, reduce pain, and enhance mobility.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Lifestyle changes, including weight management and exercise, can help reduce strain on the affected joints.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections or hyaluronic acid injections can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, when conservative treatments are not effective, surgical options may be considered. These may include joint fusion, joint replacement, or arthroscopy.
Preventing Foot and Ankle Arthritis
While not all cases of arthritis can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk and promote joint health:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the strain on your joints.
- Wear supportive and well-fitted footwear.
- Engage in regular exercise to keep your joints mobile and strong.
- Protect your feet and ankles from injuries, and seek prompt treatment for any injuries that do occur.
- Manage underlying health conditions that may contribute to arthritis, such as diabetes or gout.
Summary:
Arthritis affecting the foot and ankle can cause significant discomfort and mobility issues, with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis being common forms. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, deformities, instability, and difficulty walking. Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Treatment options include medications, physical therapy, orthotics, lifestyle modifications, injections, and, in severe cases, surgery. Dr. Ashish Suryavanshi, a prominent orthopaedic specialist in Pune, offers personalized care and expertise in managing foot and ankle arthritis. Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, wearing supportive footwear, regular exercise, injury prevention, and managing underlying health conditions. Seeking professional guidance is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of foot and ankle arthritis.