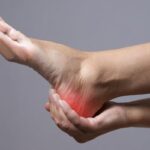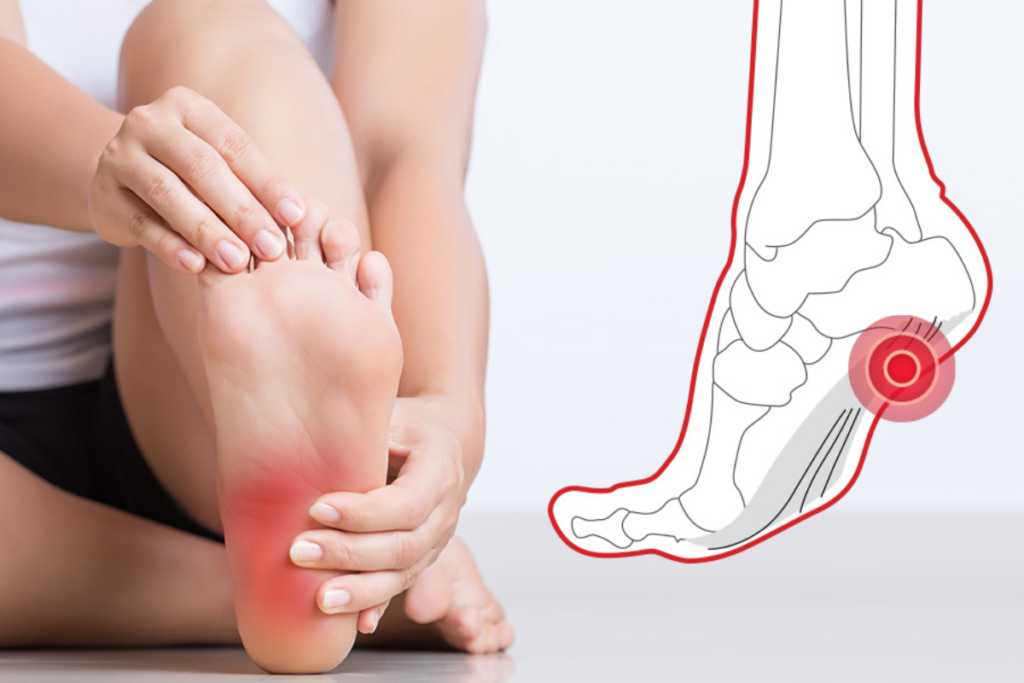
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition that causes pain in the heel and the bottom of the foot. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed or irritated. This condition can be a source of discomfort and inconvenience for many individuals, affecting their daily activities. In this blog, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for plantar fasciitis.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
The exact cause of plantar fasciitis can vary from person to person, but several factors are commonly associated with its development:
- Overuse: Repetitive activities, especially those that involve prolonged standing, walking, or running, can strain the plantar fascia and lead to inflammation.
- Age: Plantar fasciitis is more prevalent in individuals between the ages of 40 and 60.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes with inadequate arch support or cushioning can increase the risk of developing plantar fasciitis.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on the plantar fascia, making it more susceptible to inflammation.
- Tight Calf Muscles: Tight calf muscles can alter the mechanics of walking and increase strain on the plantar fascia.
- Foot Mechanics: Abnormal foot mechanics, such as flat feet or high arches, can put more stress on the plantar fascia.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis typically presents with the following symptoms:
- Heel Pain: The most common symptom is sharp, stabbing pain in the heel, often near the front or centre of the heel. Pain is usually most severe in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
- Pain After Activity: Pain tends to increase after prolonged standing, walking, or physical activity.
- Stiffness: The heel may feel stiff and less flexible.
- Tenderness: The bottom of the foot may be tender to touch, particularly near the heel.
- Discomfort When Climbing Stairs: Pain can worsen when going up or down stairs or inclines.
Treatment Options for Plantar Fasciitis
Fortunately, plantar fasciitis can often be effectively managed with conservative treatments. Here are some common approaches:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Reducing or modifying activities that exacerbate the condition is a key step. This may include avoiding prolonged standing or high-impact exercises.
- Stretching Exercises: Regular stretching of the calf muscles and the plantar fascia can help alleviate tension and reduce symptoms. Simple exercises like calf stretches, toe stretches, and the towel stretch can be beneficial.
- Orthotic Insoles: Custom or over-the-counter orthotic insoles can provide additional arch support and cushioning, reducing strain on the plantar fascia.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing shoes with good arch support, cushioning, and shock absorption can help reduce discomfort.
- Icing: Applying ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can guide you through exercises and techniques to improve foot strength, flexibility, and overall function.
- Night Splints: Wearing a night splint that keeps the foot in a dorsiflexed position can help alleviate morning heel pain.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation and pain.
Preventing Plantar Fasciitis
Preventing plantar fasciitis involves taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of developing the condition:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Managing body weight can reduce the strain on the plantar fascia.
- Choose Supportive Footwear: Opt for shoes that offer good arch support and cushioning, especially for activities that involve extended periods of standing or walking.
- Gradual Increases in Activity: When starting a new exercise program or increasing the intensity of your workouts, do so gradually to prevent overuse injuries.
- Stretch Regularly: Incorporate stretching exercises into your daily routine to maintain flexibility and prevent tight calf muscles.
When to Seek Professional Help
If conservative treatments do not provide relief or if the symptoms worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. They may recommend additional interventions, such as physical therapy, custom orthotics, or, in rare cases, surgery.
Plantar fasciitis can be a challenging condition, but with the right care and a commitment to a comprehensive treatment plan, many individuals can find relief from their symptoms and get back to enjoying their daily activities pain-free. If you suspect you have plantar fasciitis, don’t hesitate to seek professional guidance to address the issue effectively.
Summary:
Plantar fasciitis is a common foot condition characterized by inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing heel and foot pain. The causes include overuse, age, improper footwear, obesity, tight calf muscles, and abnormal foot mechanics. Symptoms include sharp heel pain, stiffness, tenderness, and discomfort during activity. Conservative treatments include rest, stretching exercises, orthotic insoles, proper footwear, icing, and medications. Prevention involves maintaining a healthy weight, choosing supportive footwear, gradual activity increases, and regular stretching. If symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare provider, such as Dr. Ashish Suryavanshi, a renowned orthopaedic specialist in Pune, is crucial. Professional guidance may lead to interventions like physical therapy, custom orthotics, or, in rare cases, surgery for effective management of plantar fasciitis.